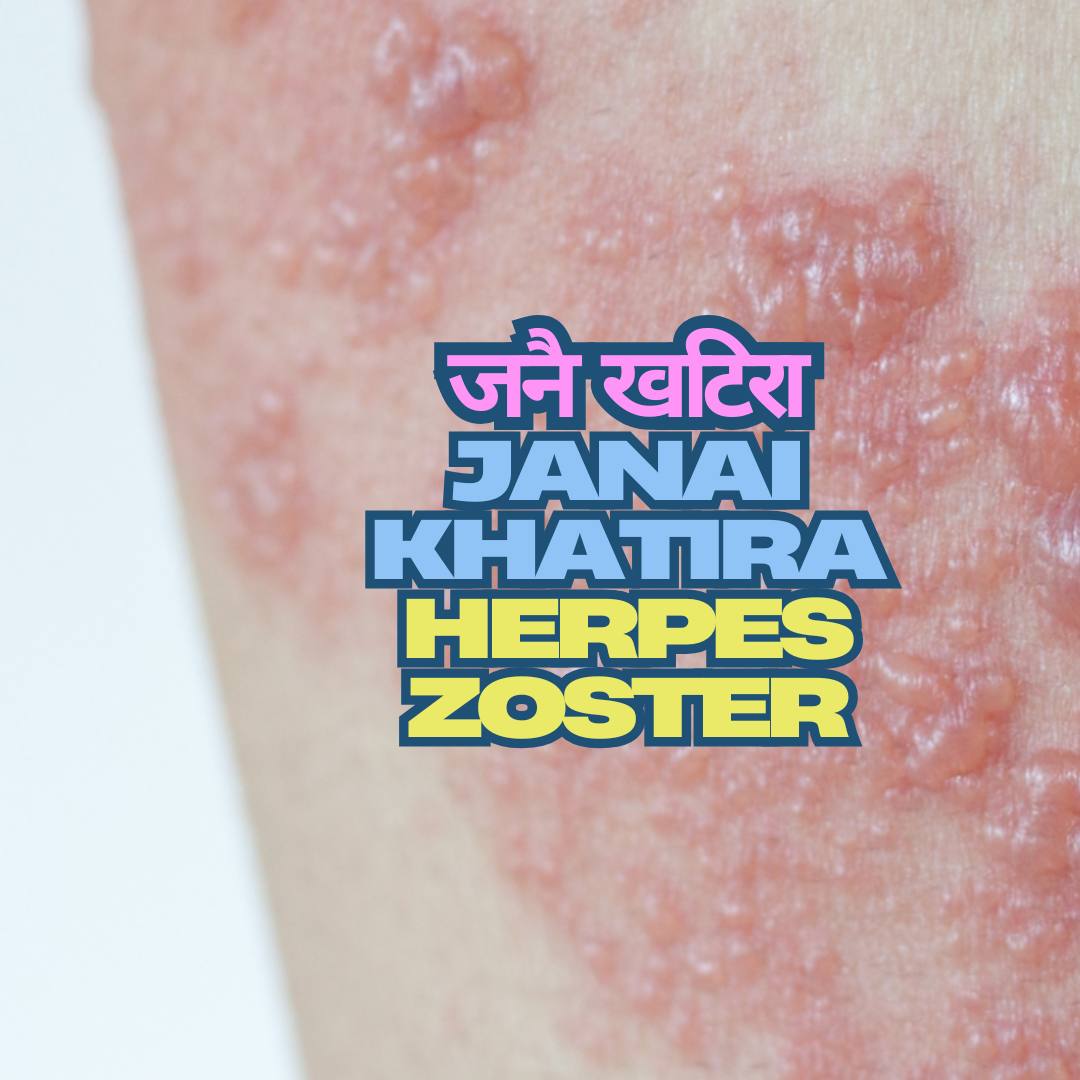
Herpes zoster, commonly known as shingles (जनै खटिरा / Janai Khatira), is a localized viral infection resulting from the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) the same virus that causes chickenpox . After someone has chickenpox, the virus stays in their body but becomes inactive in the nerve roots . Shingles occurs when this virus becomes active again later in life . It’s important to know that shingles is not the same virus that causes cold sores or genital herpes .
Herpes Zoster Article in Nepali Language: जनै खटिरा / Janai Khatira
What Happens in the Body?
When the virus reactivates, it starts to multiply in the nerve cells . The new virus particles then travel down the nerve to the skin area connected to that nerve . This causes inflammation and leads to the formation of blisters . This process explains why the shingles rash appears in a specific area on one side of the body, following the path of a nerve .
Who Gets Herpes Zoster?
The risk of getting shingles increases as people get older, and about half of all cases occur in people over 50 . It’s estimated that 10% to 30% of people who have had chickenpox will get shingles at some point .
Certain people have a higher risk of developing shingles and experiencing more severe problems . These include:
- Older adults, as their immune system naturally weakens with age .
- People with weakened immune systems due to conditions like cancer, HIV, or organ transplants .
- Individuals taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as steroids .
- People experiencing illnesses, stress, or physical injury .
Recognizing the Symptoms
Herpes Zoster usually develops in stages .
Early Signs (Pre-eruptive Phase): These can appear a few days before the rash and include :
- Pain, burning, tingling, or itching in a specific area of the skin .
- Headache .
- Feeling unwell (malaise) .
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia) .
- Fever .
- Chills .
- Fatigue .
- Upset stomach .
The Rash (Acute Eruptive Phase): This usually appears within a few days of the initial symptoms .
- A red rash develops, typically on one side of the body in a band-like pattern . It rarely crosses the midline of the body .
- The rash quickly turns into small, fluid-filled blisters called vesicles .
- New blisters can continue to appear for 3 to 5 days .
- The blisters then dry out and form scabs or crusts .
- The rash usually heals within 2 to 4 weeks, and the scabs typically fall off in about 10 days .
- Sometimes, the affected skin may have permanent changes in color or scarring .
The rash most commonly appears on the torso or face . It can wrap around the left or right side of the body . It can also occur on one side of the face, potentially affecting the forehead, scalp, and areas around the eye or ear, or on the neck .
How is Herpes Zoster Diagnosed?
Doctors usually diagnose Herpes Zoster by looking at the characteristic rash and hearing about the patient’s symptoms . The location and appearance of the rash are key clues .
In some cases, especially if the rash is not typical or in the early stages, laboratory tests might be needed . The most common and reliable test is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test, which detects the virus’s DNA in samples from the blisters . Other tests like viral culture or direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) assays are less common . Blood tests for antibodies are not usually helpful for diagnosing an active shingles infection .
Derma Clinic Offers Varicella Zoster IgG and IgM and PCR Test to diagnose Herpes Zoster if required. Do let us know if you want to do test to confirm diagnosis.
Possible Complications
Herpes Zoster can sometimes lead to complications .
- Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN): This is the most common complication, causing long-lasting nerve pain in the area of the rash, even after it has healed . The risk increases with age .
- Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO): If shingles affects the eye, it can cause serious problems like vision loss .
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: This occurs when shingles affects nerves in the face and ear, leading to facial paralysis, ear pain, hearing loss, and dizziness .
- Neurological Issues: Rarely, shingles can lead to inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) or spinal cord (myelitis), as well as nerve problems .
- Bacterial Infections: The shingles blisters can sometimes get infected with bacteria .
- Other Complications: In rare cases, shingles can cause pneumonia, hearing or balance problems, or even death, especially in people with weakened immune systems . Shingles in the mouth can lead to dental problems .
How is Herpes Zoster Treated?
The main goal of shingles treatment is to reduce pain, shorten the illness, and prevent complications .
Antiviral Medications: These medicines help to stop the virus from multiplying. They work best when started within 72 hours of the rash appearing . Common antiviral drugs include :
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
Valacyclovir and famciclovir are often preferred because the body absorbs them better and they don’t need to be taken as often as acyclovir .
Pain Relief: Pain from herpes zoster can be severe, so pain management is important .
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) or NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) or naproxen can help with mild to moderate pain .
- Prescription pain medications: For more severe pain, doctors might prescribe stronger pain relievers, including opioids like codeine, tramadol, oxycodone, or morphine .
- Topical treatments: Creams, gels, sprays, or patches containing lidocaine or capsaicin can provide localized pain relief .
- Corticosteroids: Sometimes, doctors prescribe medications like prednisone along with antivirals to reduce pain and speed up healing, especially in older adults .
- For postherpetic neuralgia: Medications like tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, nortriptyline, desipramine), anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin), and long-acting opioids may be used to manage the nerve pain . Nerve blocks or steroid injections might be options for severe pain .
Supportive Care: These measures can help with comfort and healing .
- Apply cool, wet compresses to the rash .
- Use calamine lotion to relieve itching .
- Take warm oatmeal baths for itching .
- Keep the rash clean and dry to prevent infections .
- Get enough rest and avoid stress .
- Eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly .
- Wear loose-fitting clothing .
- Avoid touching or scratching the rash to prevent spreading the virus .
Important Note
If you think you might have shingles, it’s important to see a dermatologist as soon as possible, especially if the rash is near your eye or if you have a weakened immune system . Early treatment can help reduce the severity of the illness and prevent complications .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Herpes Zoster (Janai Khatira)
Q: What is Herpes Zoster (Janai Khatira)?
A: Herpes Zoster, commonly known as Shingles (or Janai Khatira in Nepali), is a viral infection that causes a painful, localized rash. It results from the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains inactive in the nerve roots and can reactivate later in life.
Q: Is Herpes Zoster the same as genital herpes?
A: No. While the names are similar, Herpes Zoster is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is distinct from the virus responsible for cold sores or genital herpes.
Q: Who is most at risk for getting Shingles?
A: Anyone who has had chickenpox can develop shingles, but the risk increases with age. It is most common in adults over 50. Individuals with weakened immune systems due to cancer, HIV, organ transplants, or medications like steroids are also at higher risk.
Q: What are the early warning signs?
A: Before the rash appears, you may experience pain, burning, tingling, or itching in a specific area of the skin. Other early symptoms include headache, fever, chills, fatigue, and sensitivity to light.
Q: Where does the rash usually appear?
A: The rash typically forms a band-like pattern on one side of the body, most often on the torso or face. It rarely crosses the midline of the body.
Q: How is Herpes Zoster diagnosed?
A: Doctors usually diagnose it by examining the characteristic rash and reviewing your symptoms. If the diagnosis is unclear, lab tests such as a Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test can detect the virus’s DNA in blister fluid.
Q: What treatments are available?
A: Treatment includes antiviral medications like Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, or Famciclovir, which work best when started within 72 hours of the rash appearing. Pain management options range from over-the-counter pain relievers to prescription medications and topical creams.
Q: Can Shingles cause long-term complications?
A: Yes. The most common complication is Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN), which causes long-lasting nerve pain in the area where the rash occurred, even after it has healed. Other potential issues include vision loss (if the eye is affected) and skin infections.
Q: Can stress trigger an outbreak?
A: Yes, physical or emotional stress, along with illness or injury, can weaken the immune system and trigger the virus to reactivate.
Where to treat Herpes Zoster?
Derma Clinic is the Best Clinic for Herpes Zoster treatment in Kathmandu,Nepal.
Contact:
Derma Clinic
Basundhara Chowki
Tel: 9801358600
WhatsApp Us