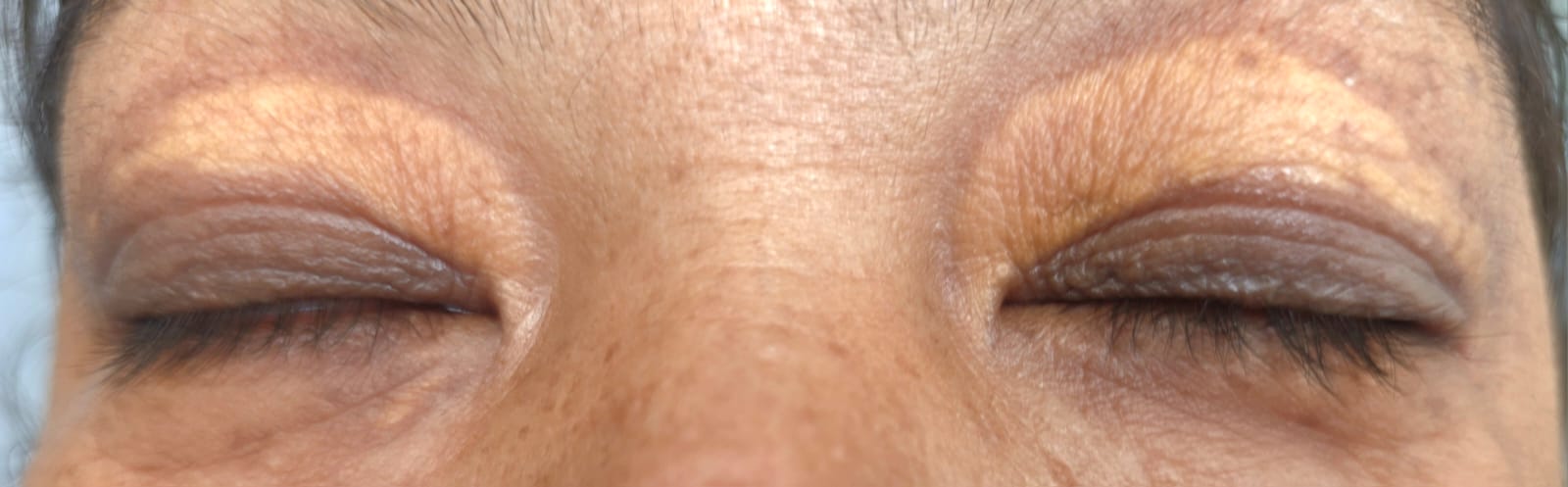
Have you noticed soft, yellowish bumps appearing on or around your eyelids? You’re not alone. These patches, known as Xanthelasma palpebrarum, are a common concern for many individuals in Nepal. While they are typically harmless, they can be a cosmetic worry and, importantly, a potential signal from your body about your underlying health.
At Derma Clinic Kathmandu, we understand your concerns. This guide will walk you through what Xanthelasma is, why it appears, and how we can effectively help you treat it.
What Exactly is Xanthelasma?
Xanthelasma appears as soft, yellowish, and slightly raised plaques. The name itself gives a clue: ‘xanthos’ is Greek for yellow, and ‘elasma’ means plate. These are essentially localized deposits of cholesterol and fats (lipids) under the surface of the skin.
Key Features & Location:
- Appearance: They are typically flat-topped or slightly elevated with a velvety or bumpy texture.
- Colour: They range from pale yellow to a more prominent, creamy-yellow hue.
- Location: Most commonly, they form on the inner corners of the upper and lower eyelids (the side closer to your nose). They can be symmetrical, appearing on both eyes.
- Symptoms: Xanthelasma itself is not painful or itchy. The primary concern is its appearance.
Why Does Xanthelasma Occur? The Underlying Reasons
The appearance of Xanthelasma is directly linked to the deposition of lipids in the skin’s dermal layer. But why does this happen? There are several reasons.
- High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia): This is the most common culprit. About 50% of people with Xanthelasma have elevated levels of lipids in their blood. This can include:
- High levels of LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein), often called “bad” cholesterol.
- Low levels of HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein), or “good” cholesterol.
- High levels of triglycerides.
- Inherited conditions like familial hypercholesterolemia, which cause unusually high cholesterol levels from a young age.
- Idiopathic (No Clear Cause): Interestingly, the other 50% of individuals with Xanthelasma have completely normal cholesterol levels. In these cases, the exact reason for the localized fat deposition is not fully understood. It might be due to a local skin abnormality that makes it prone to retaining cholesterol.
- Secondary Causes: Certain medical conditions and lifestyle factors can disrupt the body’s ability to process fats, leading to secondary hyperlipidemia and potentially causing Xanthelasma. These include:
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can affect fat metabolism.
- Thyroid problems: An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can raise cholesterol levels.
- Liver disease: Conditions like primary biliary cirrhosis can interfere with fat processing.
- Obesity and a high-fat diet.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Certain medications: Such as beta-blockers, oral contraceptives, and steroids.
It is crucial to view Xanthelasma not just as a skin issue, but as a possible indicator of a systemic health condition. A proper diagnosis at a dermatology clinic will often involve a recommendation to check your blood lipid profile.
Treatment Options for Xanthelasma
Since Xanthelasma does not go away on its own, several professional treatments are available to remove it for cosmetic reasons. Common options include:
- Surgical Excision: Cutting the lesion out with a scalpel.
- Laser Ablation: Using a focused laser beam (like a CO₂ laser) to vaporize the tissue.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the lesion with liquid nitrogen.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Using high-frequency electrical currents to remove the lesion.
- Chemical Cautry: TCA is used to treat Xanthelasma.
Each method has its pros and cons regarding effectiveness, healing time, and potential for scarring or pigmentation changes.
Experience Effective Treatment with Chemical Cautery at Derma Clinic Kathmandu
At Derma Clinic Kathmandu, we are proud to offer Chemical Cautery as a highly effective and minimally invasive treatment for Xanthelasma.
What is Chemical Cautery?
Chemical Cautery is a precise procedure where a dermatologist applies a specific chemical agent, such as trichloroacetic acid (TCA), directly onto the Xanthelasma plaque. This chemical safely breaks down the lipid-filled cells, causing the lesion to crust over and eventually fall off, revealing healthier skin underneath.
Why Choose Chemical Cautery?
- High Precision: The chemical is applied only to the targeted area, minimizing damage to the surrounding healthy skin.
- Minimally Invasive: It is a non-surgical procedure with no cutting or stitches required.
- Quick & Convenient: The procedure itself is very fast and performed in our clinic.
- Excellent Cosmetic Results: When performed by an experienced dermatologist, it yields fantastic results with a very low risk of scarring.
Don’t Let Xanthelasma Affect Your Confidence!
If you have those tell-tale yellow patches on your eyelids, it’s time to seek professional advice. Not only can we help you restore your skin’s clear appearance, but we can also guide you on the importance of checking your overall health.
The expert dermatologists at Derma Clinic Kathmandu are here to provide a thorough evaluation and offer you the best treatment plan. Our advanced Chemical Cautery procedure is a safe and reliable solution to remove Xanthelasma effectively.
Take the first step towards clearer skin today. Contact Derma Clinic Kathmandu at 9801358600 to book your consultation and learn more about our Xanthelasma treatments.